A rapid microfluidics assay for Lyme disease performed better than a standard lab workup and shows promise for use as a single diagnostic test at the point of care, according to a new study funded by the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Results for an improved version of the mChip-Ld Lyme disease test, which is being developed with support from the NIH's National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), were reported in the Journal of Clinical Microbiology online October 9.
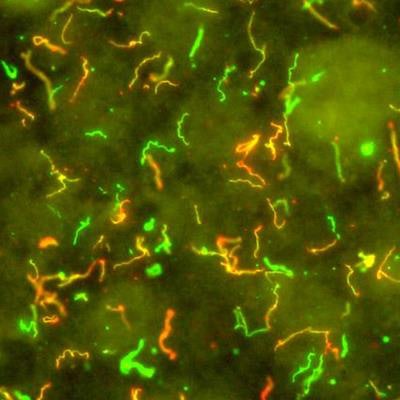
 Spiral-shaped bacteria that cause Lyme disease -- Borrelia burgdorferi -- have been illuminated using red and green fluorescent antibodies. Image courtesy of NIAID.
Spiral-shaped bacteria that cause Lyme disease -- Borrelia burgdorferi -- have been illuminated using red and green fluorescent antibodies. Image courtesy of NIAID.The researchers identified three antigens associated with high sensitivity for detecting antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi in people with early Lyme disease through a rigorous analysis of diseased samples and controls: variable major protein-like sequence lipoprotein E (VlsE), outer surface protein C type K (OspC-K), and a proprietary synthetic 33-mer peptide (PepVF). An earlier version of the assay included two of these markers, the group noted.
The performance of mChip-Ld was evaluated using samples from the Lyme Disease Biobank, the NIH, and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The researchers compared its performance with results from standard two-tier (STT) testing advised by the CDC, which calls for an enzyme immunoassay to be done first. If positive, the second step involves an immunoglobulin M/immunoglobulin G (IgM/IgG) immunoblot or an IgG-only immunoblot.
In early Lyme disease, with specificity of 95%, the mChip-Ld test's sensitivity on two panels with positive and negative samples was 80% and 85%. In late Lyme disease, sensitivity reached 100%.
With standard two-tier testing, sensitivity was 48.5% and 75% for the early Lyme disease panels and 100% for late Lyme disease. Specificity ranged from 97.5% to 100%.
"These results open the door for the development of a single, rapid, multiplexed diagnostic test for point-of-care use that can be designed to identify Lyme disease stage," reported senior author Maria Gomes-Solecki, an associate professor of microbiology, immunology, and biochemistry at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, and colleagues.
Room to improve
The standard two-tiered approach has worked relatively well but there is "plenty of room for improvement," the authors noted.
"The STT requires complex laboratory infrastructure to perform, has low sensitivity during early infection, [inter- and intralaboratory] variability, and high turnaround time and cost for the immunoblot," they wrote. "There is also confusion regarding interpretation of the immunoblot results."
Demand has been growing for better options. The CDC has stated that tests for IgM antibodies are prone to false-positive results, while IgG tests are more reliable but not as useful for early disease. With new knowledge about specific B. burgdorferi epitopes, hope is growing for a single test with no need for the immunoblot. Currently, there is no commercially available rapid point-of-care diagnostic for Lyme disease, and unmet need is high, according to the authors.
"Microfluidics offers practical advantages for miniaturizing laboratory-based tests, including portability, multiplexing, speed, and performance," they wrote.
How long might it take to get the test to market? Gomes-Solecki told LabPulse.com that further testing is needed in the clinic to assess the test's potential at the point of care. However, the researchers first need to discuss with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration the next steps for the assay's development, she said in an emailed response to questions. They are also exploring options with potential commercial partners.